01-04-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Chemical Equilibrium [EN]-[IT]
13 comments

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

01-04-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Chemical Equilibrium [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a short instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_59)
Chemical Equilibrium

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
Today I will try to write something about chemical equilibrium. In chemistry, chemical equilibrium is a condition in which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
Direct reaction means that process where the reactants are transformed into products.
Inverse reaction means that process where the products are transformed into reactants. Having said that, we can now also understand that this leads to a situation in which the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time. Now we must clarify one thing, this constancy that remains over time occurs even if the reactions are continuing. In fact, it is good to clarify that equilibrium does not mean that the reactions are stopped, but this actually demonstrates that in that context there is a dynamic balance, that is, the reactions balance each other dynamically.
Balance - ammonia synthesis
One of the most used examples to explain chemical equilibrium is the equilibrium between N2, H2 and NH3 in the synthesis of ammonia.
Where:
𝑁₂ = Molecular Nitrogen
𝐻₂ = Molecular Hydrogen
𝑁𝐻₃ = Ammonia
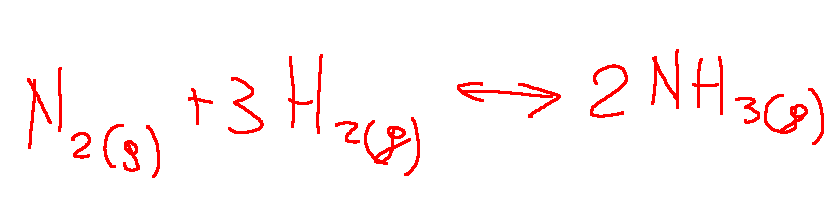
The chemical formula above represents the ammonia synthesis reaction. This is an important process in industrial chemistry.
This reaction shows how molecular nitrogen and molecular hydrogen react to form ammonia. This is a chemical equilibrium reaction that occurs under specific conditions.
Note: Ammonia synthesis is essential for the production of fertilizers, so it plays an important role in agriculture.
Ammonia Synthesis in Detail

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Looking at the chemical formula above we can also go into the technical details of ammonia synthesis.
Here is a technical explanation of the synthesis of ammonia, the first part may seem difficult to understand, but in the end the description will end with a less technical and understandable language that could also clarify what was written before the final considerations... let's start with the explanation....
Suppose we introduce the reagents nitrogen and hydrogen inside a reactor with a fixed volume V. In the reactor there is a catalyst based on iron oxide, which allows the reaction to occur at an acceptable speed (catalyst). Finally we bring the reactor to a temperature T. If we measure the concentration of each chemical species inside the reactor we note that that of the reagents decreases over time (the reagents are consumed) while that of the ammonia produced increases. After a certain time, however, the concentrations reach a stationary value. Leaving the reactor at the same temperature T even for an extremely long time we do not observe any change in the chemical composition of the reaction mixture. We then say that the system has reached equilibrium. The corresponding reaction is indicated with a double arrow, whose meaning is simple: if on the one hand ammonia is the product of the reaction between N2 and H2 (direct reaction), on the other hand ammonia itself can decompose, reforming N2 and H2 (reverse reaction).
Final considerations
At equilibrium, it is assumed that the speed of the direct reaction is exactly equal to the speed of the reverse reaction (dynamic equilibrium).
Homogeneous phase reaction equilibrium
In the field of chemistry, and more precisely speaking about chemical equilibria, we have a key concept. In the chemistry of chemical equilibrium we can also talk about homogeneous phase reaction equilibrium. Homogeneous phase reaction equilibrium concerns chemical reactions in which all the reagents and products are in the same phase. We mainly talk about gas or aqueous solution.
Earlier we introduced the concept of chemical equilibrium, a context in which the concentrations of reagents and products remain constant over time even if chemical reactions continue to occur.
So when do we talk about homogeneous phase reaction equilibrium?
When all the components of the reaction are in the same physical phase, we talk about homogeneous equilibrium.
Conclusions
In chemistry it is fundamental to study the equilibrium of reactions because it allows us to understand, predict and control how chemical reactions behave in reality. This is useful for optimizing industrial processes, for controlling rather complex chemical reactions and for calculating concentrations. Some define the study of chemical equilibrium as the compass of chemistry, because this study allows us to understand where a reaction is going.
Question
Did you know that the synthesis of ammonia is an equilibrium in a homogeneous phase? That is, did you know that it is a reversible reaction that can go either towards the formation of ammonia, or towards dissociation into reagents?

ITALIAN

01-04-2025 - Basi di chimica - Equilibrio chimico [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_59)
Equilibrio chimico

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
Oggi proverò a scrivere qualcosa a riguardo dell’equilibrio chimico. In chimica, l’equilibrio chimico, è una condizione in cui la velocità della reazione diretta è uguale alla velocità della reazione inversa.
Per reazione diretta si intende quel processo dove i reagenti si trasformano in prodotti.
Per reazione inversa si intende quel processo dove i prodotti si trasformano in reagenti.detto questo ora possiamo anche comprendere che questo porta ad una situazione in cui le concentrazioni di reagenti e prodotti rimangono costanti nel tempo. Ora dobbiamo chiarire una cosa, questa costanza che rimane nel tempo avviene anche se le reazioni stanno continuando. Infatti è bene chiarire che l’equilibrio non significa che le reazioni siano ferme, ma questo in realtà dimostra che esiste in quel contesto un bilanciamento dinamico, cioè le reazioni si bilanciano dinamicamente.
Bilanciamento - sintesi dell'ammoniaca
Uno tra gli esempi più utilizzati per spiegare l'equilibrio chimico è l'equilibrio tra N2, H2 e NH3 nella sintesi dell'ammoniaca.
Dove:
𝑁₂ = Azoto molecolare
𝐻₂ = Idrogeno molecolare
𝑁𝐻₃ = Ammoniaca
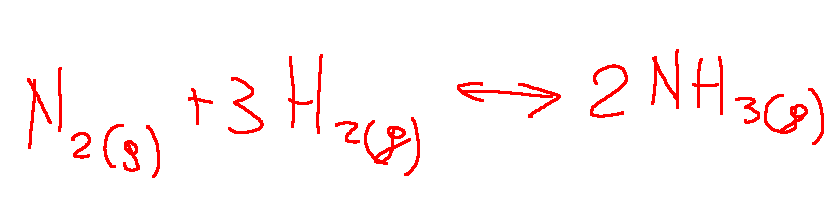
La formula chimica riportata qui sopra rappresenta appunto la reazione di sintesi dell’ammoniaca. Questo è un processo importante nella chimica industriale.
Questa reazione mostra come l’azoto molecolare e l’idrogeno molecolare reagiscono per formare l’ammoniaca. Questa è proprio una reazione di equilibrio chimico che si svolge sotto specifiche condizioni.
Nota: la sintesi dell’ammoniaca è fondamentale per la produzione di fertilizzanti, quindi svolge un ruolo importante nell’agricoltura.
Sintesi dell'ammoniaca nel dettaglio

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Riguardando la formula chimica riportata sopra possiamo entrare anche nel dettaglio tecnico della sintesi dell'ammoniaca.
Qui di seguito una spiegazione tecnica della sintesi dell'ammoniaca, la prima parte potrà sembrare difficile da comprendere, ma alla fine la descrizione terminerà con un linguaggio meno tecnico e comprensibile che potrebbe chiarire anche ciò che è stato scritto prima delle considerazioni finali... partiamo con la spiegazione....
Supponiamo di introdurre i reagenti azoto e idrogeno all’interno di un reattore con un volume fisso V. Nel reattore è presente un catalizzatore a base di ossido di ferro, che consente alla reazione di avvenire con una velocità accettabile (catalizzatore). Infine portiamo il reattore ad una temperatura T. Se si misura la concentrazione di ciascuna specie chimica all’interno del reattore si nota che quella dei reagenti diminuisce nel tempo (i reagenti si consumano) mentre quella dell’ammoniaca prodotta aumenta. Dopo un certo tempo, tuttavia, le concentrazioni raggiungono un valore stazionario. Lasciando il reattore alla stessa temperatura T anche per un tempo estremamente lungo non si osserva alcun cambiamento nella composizione chimica della miscela di reazione. Si dice allora che il sistema ha raggiunto l’equilibrio. La reazione corrispondente viene indicata con una doppia freccia, il cui significato è semplice: se da una parte l’ammoniaca è il prodotto della reazione tra N2 e H2 (reazione diretta), dall’altra l’ammoniaca stessa può decomporsi riformando N2 e H2 (reazione inversa).
Considerazioni finali
All’equilibrio si assume che la velocità della reazione diretta sia esattamente uguale alla velocità della reazione inversa (equilibrio dinamico).
Equilibrio di reazioni in fase omogenea
Nell’ambito della chimica, e più precisamente parlando proprio degli equilibri chimici, abbiamo un concetto chiave. Nella chimica dell’equilibrio chimico possiamo parlare anche di equilibrio di reazioni in fase omogenea. L’equilibrio di reazioni in fase omogenea riguarda reazioni chimiche in cui tutti i reagenti e i prodotti si trovano nella stessa fase. Principalmente parliamo di gas oppure soluzione acquosa.
Prima abbiamo introdotto il concetto di equilibrio chimico, un contesto in cui le concentrazioni di reagenti e prodotti restano costanti nel tempo anche se le reazioni chimiche continuano a verificarsi.
Allora quand’è che parliamo di equilibrio di reazioni in fase omogenea?
Quando tutti i componenti della reazione sono nella stessa fase fisica, parliamo di equilibrio omogeneo.
Conclusioni
In chimica è fondamentale studiare l’equilibrio delle reazioni perché permette di comprendere, prevedere e controllare come nella realtà si comportano le reazioni chimiche. Questo è utile per ottimizzare i processi industriali, per controllare reazioni chimiche piuttosto complesse e per calcolare le concentrazioni. Qualcuno definisce lo studio dell’equilibrio chimico come la bussola della chimica, perché questo studio ci permette di capire dove sta andando una reazione.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che la sintesi dell'ammoniaca è un equilibrio in fase omogenea? Cioè sapevate che è una reazione reversibile che può andare sia verso la formazione dell'ammoniaca, sia verso la dissociazione nei reagenti?
THE END

Comments