DSA (Medium) — Linked List — Maximum Twin Sum of a Linked List (Python, Typescript & Go)
0 comments

In a linked list of size n, where n is even, the ith node (0-indexed) of the linked list is known as the twin of the (n-1-i)th node, if 0 <= i <= (n / 2) - 1.
- For example, if n = 4, then node 0 is the twin of node 3, and node 1 is the twin of node 2. These are the only nodes with twins for n = 4.
The twin sum is defined as the sum of a node and its twin.
Given the head of a linked list with even length, return the maximum twin sum of the linked list.
Example 1:

Input: head = [5,4,2,1]
Output: 6
Explanation:
Nodes 0 and 1 are the twins of nodes 3 and 2, respectively. All have twin sum = 6.
There are no other nodes with twins in the linked list.
Thus, the maximum twin sum of the linked list is 6.
Example 2:
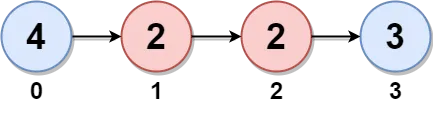
Input: head = [4,2,2,3]
Output: 7
Explanation:
The nodes with twins present in this linked list are:
- Node 0 is the twin of node 3 having a twin sum of 4 + 3 = 7.
- Node 1 is the twin of node 2 having a twin sum of 2 + 2 = 4.
Thus, the maximum twin sum of the linked list is max(7, 4) = 7.
Example 3:
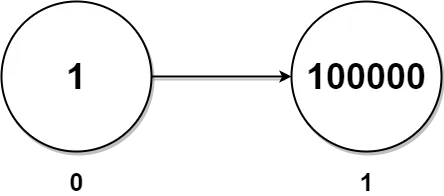
Input: head = [1,100000]
Output: 100001
Explanation:
There is only one node with a twin in the linked list having twin sum of 1 + 100000 = 100001.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is an even integer in the range [2, 105].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 105
Explanation
Imagine you have a line of numbers connected together, like a train. You want to find the biggest sum you can get by adding the first number to the last, the second number to the second-to-last, and so on.
🚅Find the Middle:
- Walk along the train with two people: one walking normally (slow), and one walking twice as fast (fast).
- When the fast walker reaches the end, the slow walker will be in the middle of the train.
🚅Reverse the Second Half:
- Take the second half of the train (from the middle to the end) and turn it around, so the last car becomes the first.
🚅Calculate Twin Sums:
- Now, walk along the first half of the train and the reversed second half at the same time.
- Add the number in the current car of the first half to the number in the current car of the reversed second half.
- Keep track of the biggest sum you find.
🚅Return the Biggest Sum:
- Once you’ve added all the pairs, tell me the biggest sum you found.
Simplified Example
Let’s say the train is: [5, 4, 2, 1]
🚅Find the Middle: The middle is between 4 and 2.
🚅Reverse the Second Half: The second half [2, 1] becomes [1, 2].
🚅Calculate Twin Sums:
- 5 + 1 = 6
- 4 + 2 = 6
Return the Biggest Sum: The biggest sum is 6.
Implementations
Python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def pairSum(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> int:
"""
Finds the maximum twin sum in a linked list with even length.
Args:
head: The head of the linked list.
Returns:
The maximum twin sum.
"""
if not head or not head.next:
return 0
# 1. Find the middle of the linked list
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# 2. Reverse the second half of the linked list
prev = None
curr = slow
while curr:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
# 3. Calculate twin sums and find the maximum
max_sum = 0
left = head
right = prev
while right:
max_sum = max(max_sum, left.val + right.val)
left = left.next
right = right.next
return max_sum
Typescript
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function pairSum(head: ListNode | null): number {
if (!head || !head.next) {
return 0;
}
// 1. Find the middle of the linked list
let slow: ListNode | null = head;
let fast: ListNode | null = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
if (slow) {
slow = slow.next;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 2. Reverse the second half of the linked list
let prev: ListNode | null = null;
let curr: ListNode | null = slow;
while (curr) {
const nextNode: ListNode | null = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextNode;
}
// 3. Calculate twin sums and find the maximum
let maxSum: number = 0;
let left: ListNode | null = head;
let right: ListNode | null = prev;
while (right) {
if (left && right) {
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, left.val + right.val);
left = left.next;
right = right.next;
}
}
return maxSum;
}
Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func pairSum(head *ListNode) int {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return 0
}
// 1. Find the middle of the linked list
slow := head
fast := head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
// 2. Reverse the second half of the linked list
var prev *ListNode
curr := slow
for curr != nil {
next := curr.Next
curr.Next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
}
// 3. Calculate twin sums and find the maximum
maxSum := 0
left := head
right := prev
for right != nil {
sum := left.Val + right.Val
if sum > maxSum {
maxSum = sum
}
left = left.Next
right = right.Next
}
return maxSum
}
If you liked this content I’d appreciate an upvote or a comment. That helps me improve the quality of my posts as well as getting to know more about you, my dear reader.
Muchas gracias!
Follow me for more content like this.
X | PeakD | Rumble | YouTube | Linked In | GitHub | PayPal.me | Medium
Down below you can find other ways to tip my work.
BankTransfer: "710969000019398639", // CLABE
BAT: "0x33CD7770d3235F97e5A8a96D5F21766DbB08c875",
ETH: "0x33CD7770d3235F97e5A8a96D5F21766DbB08c875",
BTC: "33xxUWU5kjcPk1Kr9ucn9tQXd2DbQ1b9tE",
ADA: "addr1q9l3y73e82hhwfr49eu0fkjw34w9s406wnln7rk9m4ky5fag8akgnwf3y4r2uzqf00rw0pvsucql0pqkzag5n450facq8vwr5e",
DOT: "1rRDzfMLPi88RixTeVc2beA5h2Q3z1K1Uk3kqqyej7nWPNf",
DOGE: "DRph8GEwGccvBWCe4wEQsWsTvQvsEH4QKH",
DAI: "0x33CD7770d3235F97e5A8a96D5F21766DbB08c875"
Comments